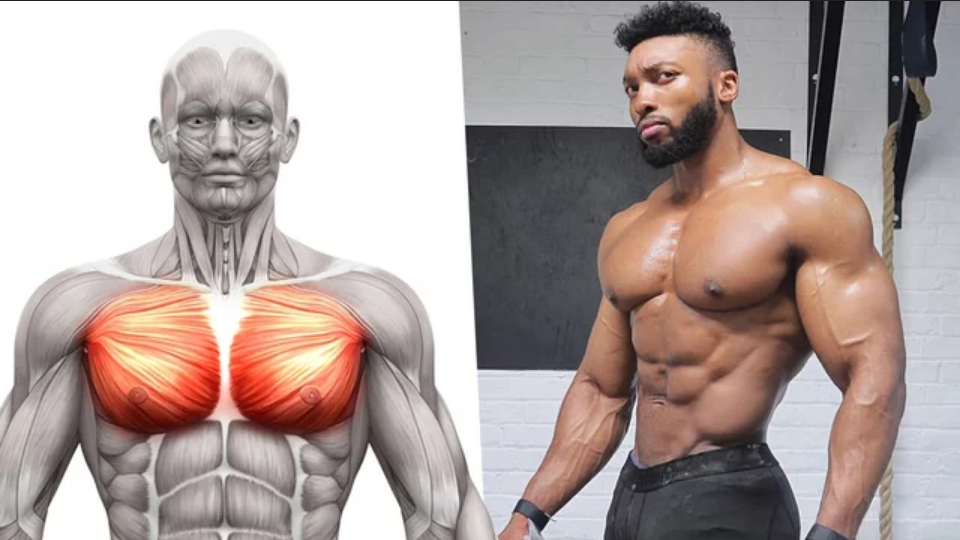
Struggling to grow a thick and strong chest? Use this excellent critique from the legend that was John Meadows.
Scroll down to the video to find all the reasons.
Having a strong chest can provide several benefits, including:
Improved posture: A strong chest can help to improve posture by pulling the shoulders back and opening up the chest.
Increased upper body strength: A strong chest is essential for many upper body exercises such as push-ups, bench press, and dips, which can improve overall upper body strength.
Enhanced athletic performance: A strong chest can help athletes to generate more power and force during movements such as throwing, punching, or pushing.
Reduced risk of injury: A strong chest can help to stabilize the shoulders and reduce the risk of injury during activities that involve the upper body.
Improved appearance: A strong chest can help to improve the appearance of the chest and upper body, which can boost confidence and self-esteem.
The chest muscles, also known as the pectoral muscles or “pecs,” are a group of muscles that are located in the front of the chest. There are two main muscles in the chest:
There are also several smaller muscles in the chest, including:
The number of reps and sets that is best for building muscle can vary depending on several factors, including the individual’s fitness level, goals, and the specific exercise being performed. However, some general guidelines to consider are:
For building muscle size (hypertrophy), a range of 8-12 reps per set is generally recommended. This range is considered to be the “sweet spot” for muscle growth.
For building muscle strength, a lower rep range of 1-5 reps per set is generally recommended. This range allows for heavier weights to be lifted and can lead to improvements in strength.
For building muscular endurance, a higher rep range of 15-20 reps per set is generally recommended. This range focuses on increasing the ability of the muscle to work for extended periods without fatigue.
For sets, a range of 3-5 sets per exercise is generally recommended for muscle growth. This allows for enough volume to stimulate muscle growth without causing excessive fatigue.
It’s important to note that these are general guidelines, and the optimal number of reps and sets for an individual may vary based on their specific goals and needs. It’s also important to progressively increase weight or resistance as you get stronger to continue challenging your muscles and stimulate growth.
Macronutrients are the three main types of nutrients that are required in relatively large amounts by the human body to maintain proper health and function. The three main macronutrients are:
Each of these macronutrients provides the body with energy, but they are metabolized and used differently by the body. The body requires these macronutrients in varying amounts depending on factors such as age, sex, weight, physical activity, and overall health status. A balanced diet that includes all three macronutrients in the appropriate amounts can help to ensure optimal health and function.
Protein is important for muscle growth because it provides the building blocks (amino acids) that the body needs to repair and build muscle tissue. When we exercise, we create small tears in our muscle fibers, and the body needs protein to repair these tears and build stronger muscles.
Protein is also essential for the production of new muscle tissue. Without adequate protein intake, the body will not have the necessary amino acids to synthesize new muscle tissue, and muscle growth will be limited.
In addition to its role in muscle growth and repair, protein also helps to regulate metabolism and maintain overall health. Protein is involved in many important bodily functions, including the production of enzymes, hormones, and other essential molecules.
For optimal muscle growth, it is recommended that individuals consume about 1-1.6 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day. This can be achieved through a combination of dietary protein sources such as lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, beans, and legumes, as well as protein supplements such as whey protein, casein protein, and plant-based protein powders.
Sleep is vital for recovery and exercise because it is during sleep that the body undergoes many important physiological processes that are critical for recovery and growth. These processes include:
Muscle repair and growth: During sleep, the body releases hormones such as human growth hormone (HGH) and testosterone, which are important for repairing and building muscle tissue.
Tissue repair and regeneration: Sleep also plays a key role in tissue repair and regeneration, allowing the body to repair damaged tissues and heal from injuries.
Energy restoration: Sleep is important for restoring energy levels, which can help to improve performance during exercise.
Mental and emotional health: Sleep is important for overall mental and emotional health, which can help to reduce stress and anxiety, improve mood, and increase motivation for exercise.
Hormone regulation: Sleep is also important for regulating hormones such as cortisol and insulin, which play important roles in metabolism, energy regulation, and muscle growth.
Without adequate sleep, the body may not have enough time to complete these important physiological processes, which can lead to decreased performance, increased risk of injury, and slower recovery times. For optimal recovery and exercise performance, it is recommended that adults get 7-9 hours of sleep per night.